
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) set basic guidelines of financial reporting so that the financial statements of a company can be reliable, transparent, and are comparable across the other companies around the globe. Prior to IFRS, every country has different Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) for the businesses to prepare financial statements in their own country. With globalization, it was becoming difficult to undertake cross border transactions, because it was difficult to understand financial statements prepared in different GAAP. To bring harmony in the accounting language, the International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC) started developing the International Accounting Standards (IAS) from the year 1973. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) took over the functions from IASC in July 2000. Since then a set of common reporting standards is referred to as IFRS. IFRS has picked up some foothold over the most recent few years, which is vindicated by the way that around 144 out of 166 jurisdictions of the world have adopted IFRS for all or most domestic publicly accountable entities (listed companies and financial institutions).
IFRS are principle-based standards as against rule-based standards. It allows entities to make estimates and judgments based on size and circumstances of the business. There are total 41 reporting standards and 18 interpretations in the set of IFRS, as mentioned below:
A – Guidance issued by IASC before July 2000 and later on adopted by IASB
- International Accounting Standards (IAS): IAS 1 to 41 (Total 24 standards)
- Standard Interpretation Committee (SIC) – (Total 5)
B – Guidance issued by IASB after July 2000
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS): IFRS 1 to 17 (Total 17 standards)
- IFRS Interpretation Committee (IFRS IC) – (Total 13)

IFRS in India
India has not adopted IFRS as is, however, decided to adopt reporting standards which are based on IFRS. In India, those standards are called as Indian Accounting Standards Converged with IFRS (Ind AS).. Ind AS is framed with minor deviations in IFRS, called as carve outs. Ind AS is applicable to a certain set of companies from the year 2016-17. Ind AS road map in India is as below:
Mandatory Adoption
Companies (other than banks, NBFCs and Insurance Companies):
- Listed Companies or Companies in the process of the Listing (debt or equity listed in or outside India).
- All other unlisted Companies having net worth of INR 250 crores or more.
- Holding, Subsidiary, joint venture or associates of companies covered above.
- Companies newly satisfying the threshold above will comply with Ind AS immediately from subsequent year
NBFCs (NA to banks and insurance companies either voluntarily or statutorily):
- Listed NBFCs or NBFCs in the process of Listing (debt or equity listed in or outside India).
- All other unlisted NBFCs having net worth of INR 250 Crores
- Holding, Subsidiary, Joint venture or Associates of companies covered above
- By 31 March 2020, all the Companies and NBFC’s above are required to comply with Ind AS. Not applicable to banks and insurance companies
Voluntary Adoption
Companies can voluntarily converge with Ind AS. However, banks and Insurance companies are not allowed to adopt Ind AS voluntarily.
Key Considerations
- Audited stand-alone financial statements as on 31 March to be considered for the calculation of net worth.
- Net worth does not include revaluation reserves, write back of depreciation and amalgamation reserve
- Once Ind AS is followed, it shall be followed for all subsequent years.
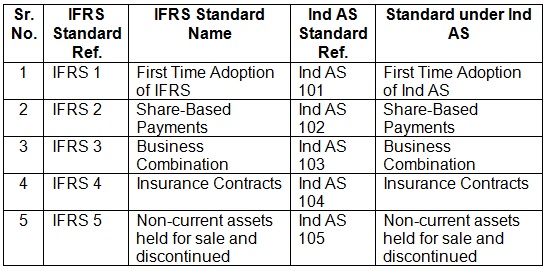
Numbering Mechanism of Reporting Standards – IFRS vis-à-vis Ind AS
| Sr. No. | IFRS Standard Ref. | IFRS Standard Name | Ind AS Standard Ref. | Standard under Ind AS |
| 1 | IFRS 1 | First Time Adoption of IFRS | Ind AS 101 | First Time Adoption of Ind AS |
| 2 | IFRS 2 | Share-Based Payments | Ind AS 102 | Share-Based Payments |
| 3 | IFRS 3 | Business Combination | Ind AS 103 | Business Combination |
| 4 | IFRS 4 | Insurance Contracts | Ind AS 104 | Insurance Contracts |
| 5 | IFRS 5 | Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations | Ind AS 105 | Non-current assets held for sale and discontinued operations |
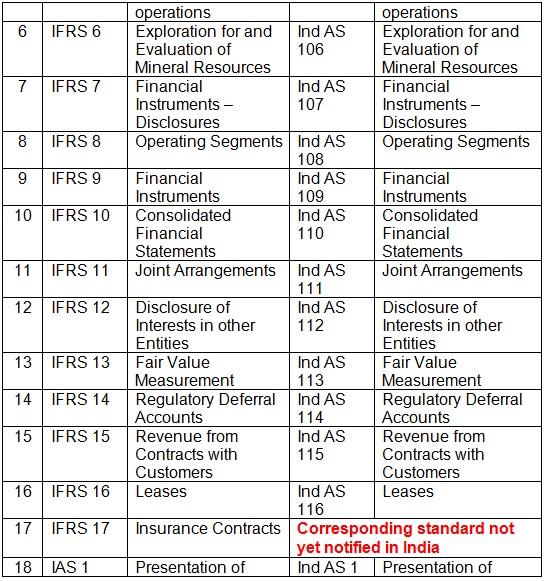
| 6 | IFRS 6 | Exploration for and Evaluation of Mineral Resources | Ind AS 106 | Exploration for and Evaluation of Mineral Resources |
| 7 | IFRS 7 | Financial Instruments – Disclosures | Ind AS 107 | Financial Instruments – Disclosures |
| 8 | IFRS 8 | Operating Segments | Ind AS 108 | Operating Segments |
| 9 | IFRS 9 | Financial Instruments | Ind AS 109 | Financial Instruments |
| 10 | IFRS 10 | Consolidated Financial Statements | Ind AS 110 | Consolidated Financial Statements |
| 11 | IFRS 11 | Joint Arrangements | Ind AS 111 | Joint Arrangements |
| 12 | IFRS 12 | Disclosure of Interests in other Entities | Ind AS 112 | Disclosure of Interests in other Entities |
| 13 | IFRS 13 | Fair Value Measurement | Ind AS 113 | Fair Value Measurement |
| 14 | IFRS 14 | Regulatory Deferral Accounts | Ind AS 114 | Regulatory Deferral Accounts |
| 15 | IFRS 15 | Revenue from Contracts with Customers | Ind AS 115 | Revenue from Contracts with Customers |
| 16 | IFRS 16 | Leases | Ind AS 116 | Leases |
| 17 | IFRS 17 | Insurance Contracts | Corresponding standard not yet notified in India | |
| 18 | IAS 1 | Presentation of Financial Statements | Ind AS 1 | Presentation of Financial Statements |
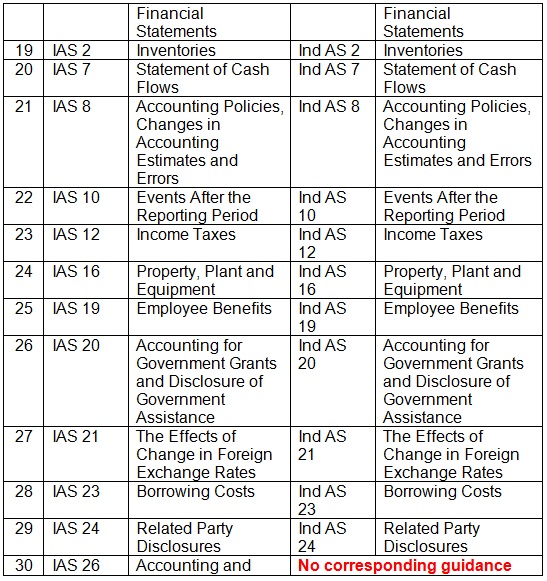
| 19 | IAS 2 | Inventories | Ind AS 2 | Inventories |
| 20 | IAS 7 | Statement of Cash Flows | Ind AS 7 | Statement of Cash Flows |
| 21 | IAS 8 | Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors | Ind AS 8 | Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors |
| 22 | IAS 10 | Events After the Reporting Period | Ind AS 10 | Events After the Reporting Period |
| 23 | IAS 12 | Income Taxes | Ind AS 12 | Income Taxes |
| 24 | IAS 16 | Property, Plant and Equipment | Ind AS 16 | Property, Plant and Equipment |
| 25 | IAS 19 | Employee Benefits | Ind AS 19 | Employee Benefits |
| 26 | IAS 20 | Accounting for Government Grants and Disclosure of Government Assistance | Ind AS 20 | Accounting for Government Grants and Disclosure of Government Assistance |
| 27 | IAS 21 | The Effects of Change in Foreign Exchange Rates | Ind AS 21 | The Effects of Change in Foreign Exchange Rates |
| 28 | IAS 23 | Borrowing Costs | Ind AS 23 | Borrowing Costs |
| 29 | IAS 24 | Related Party Disclosures | Ind AS 24 | Related Party Disclosures |
| 30 | IAS 26 | Accounting and Reporting by Retirement Benefit Plans | No corresponding guidance under Ind AS | |
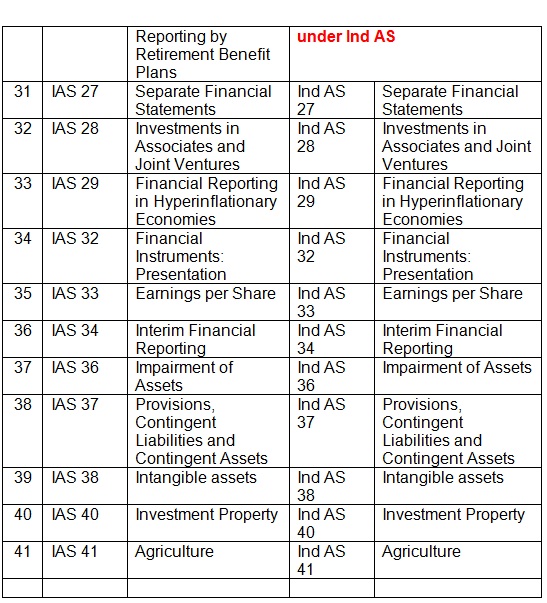
| 31 | IAS 27 | Separate Financial Statements | Ind AS 27 | Separate Financial Statements |
| 32 | IAS 28 | Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures | Ind AS 28 | Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures |
| 33 | IAS 29 | Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies | Ind AS 29 | Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies |
| 34 | IAS 32 | Financial Instruments: Presentation | Ind AS 32 | Financial Instruments: Presentation |
| 35 | IAS 33 | Earnings per Share | Ind AS 33 | Earnings per Share |
| 36 | IAS 34 | Interim Financial Reporting | Ind AS 34 | Interim Financial Reporting |
| 37 | IAS 36 | Impairment of Assets | Ind AS 36 | Impairment of Assets |
| 38 | IAS 37 | Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets | Ind AS 37 | Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets |
| 39 | IAS 38 | Intangible assets | Ind AS 38 | Intangible assets |
| 40 | IAS 40 | Investment Property | Ind AS 40 | Investment Property |
| 41 | IAS 41 | Agriculture | Ind AS 41 | Agriculture |
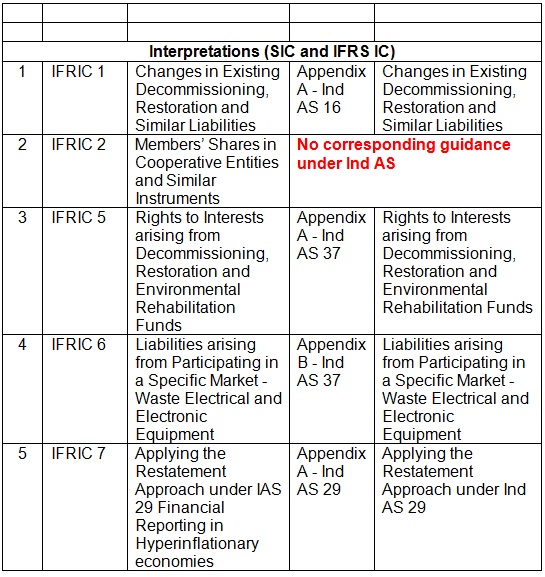
Interpretations (SIC and IFRS IC) |
||||
| 1 | IFRIC 1 | Changes in Existing Decommissioning, Restoration and Similar Liabilities | Appendix A – Ind AS 16 | Changes in Existing Decommissioning, Restoration and Similar Liabilities |
| 2 | IFRIC 2 | Members’ Shares in Cooperative Entities and Similar Instruments | No corresponding guidance under Ind AS | |
| 3 | IFRIC 5 | Rights to Interests arising from Decommissioning, Restoration and Environmental Rehabilitation Funds | Appendix A – Ind AS 37 | Rights to Interests arising from Decommissioning, Restoration and Environmental Rehabilitation Funds |
| 4 | IFRIC 6 | Liabilities arising from Participating in a Specific Market – Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment | Appendix B – Ind AS 37 | Liabilities arising from Participating in a Specific Market -Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment |
| 5 | IFRIC 7 | Applying the Restatement Approach under IAS 29 Financial Reporting in
Hyperinflationary economies |
Appendix A – Ind AS 29 | Applying the Restatement Approach under Ind AS 29 |
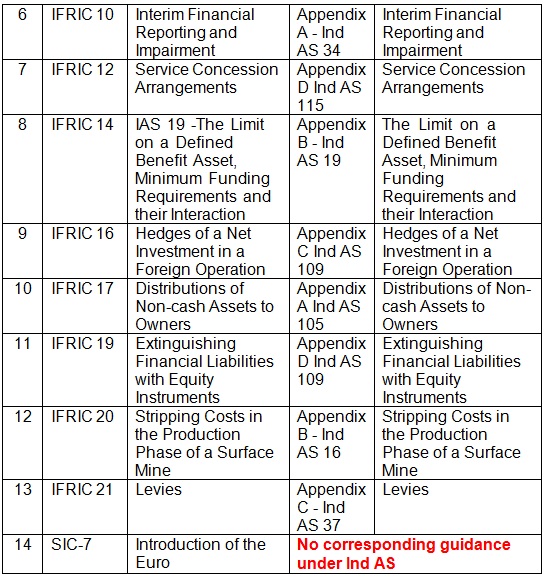
| 6 | IFRIC 10 | Interim Financial Reporting and Impairment | Appendix A – Ind AS 34 | Interim Financial Reporting and Impairment |
| 7 | IFRIC 12 | Service Concession Arrangements | Appendix D Ind AS 115 | Service Concession Arrangements |
| 8 | IFRIC 14 | IAS 19 -The Limit on a Defined Benefit Asset, Minimum Funding Requirements and their Interaction | Appendix B – Ind AS 19 | The Limit on a Defined Benefit Asset, Minimum Funding Requirements and their Interaction |
| 9 | IFRIC 16 | Hedges of a Net Investment in a Foreign Operation | Appendix C Ind AS 109 | Hedges of a Net Investment in a Foreign Operation |
| 10 | IFRIC 17 | Distributions of Non-cash Assets to Owners | Appendix A Ind AS 105 | Distributions of Non-cash Assets to Owners |
| 11 | IFRIC 19 | Extinguishing Financial Liabilities with Equity Instruments | Appendix D Ind AS 109 | Extinguishing Financial Liabilities with Equity Instruments |
| 12 | IFRIC 20 | Stripping Costs in the Production Phase of a Surface Mine | Appendix B – Ind AS 16 | Stripping Costs in the Production Phase of a Surface Mine |
| 13 | IFRIC 21 | Levies | Appendix C – Ind AS 37 | Levies |
| 14 | SIC-7 | Introduction of the Euro | No corresponding guidance under Ind AS | |
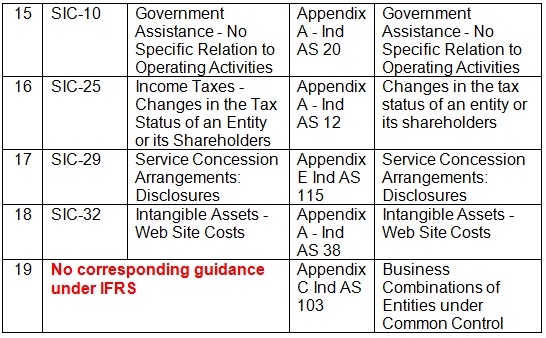
| 15 | SIC-10 | Government Assistance – No Specific Relation to Operating Activities | Appendix A – Ind AS 20 | Government Assistance – No Specific Relation to Operating Activities |
| 16 | SIC-25 | Income Taxes – Changes in the Tax Status of an Entity or its Shareholders | Appendix A – Ind AS 12 | Changes in the tax status of an entity or its shareholders |
| 17 | SIC-29 | Service Concession Arrangements: Disclosures | Appendix E Ind AS 115 | Service Concession Arrangements: Disclosures |
| 18 | SIC-32 | Intangible Assets – Web Site Costs | Appendix A – Ind AS 38 | Intangible Assets -Web Site Costs |
| 19 | No corresponding guidance under IFRS | Appendix C Ind AS 103 | Business Combinations of Entities under Common Control | |
- Total reporting standards issued under IFRS are 41. Total reporting standards issued under Ind AS are 39.
- Total interpretations under IFRS (IFRS IC + SIC) are 18. Total interpretation included under Ind AS (Appendix to relevant standards) are 17.
Numbering Mechanism of Reporting Standards – IFRS vis-à-vis Ind AS
- Total reporting standards issued under IFRS are 41. Total reporting standards issued under Ind AS are 39.
- Total interpretations under IFRS (IFRS IC + SIC) are 18. Total interpretation included under Ind AS (Appendix to relevant standards) are 17.

We, FinPro consulting, provide quality consulting and training services who belong to accounts and finance background. Our 108 hours of recorded video lectures on IFRS can help you to upgrade your IFRS / Ind AS knowledge. Candidates undergoing video lectures can also appear for the Diploma in IFRS (DipIFR) examination accredited by the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA), UK. Further, we organize live-online training sessions on weekends for those who are preparing for DipIFR Examination.







